Cervical Cancer
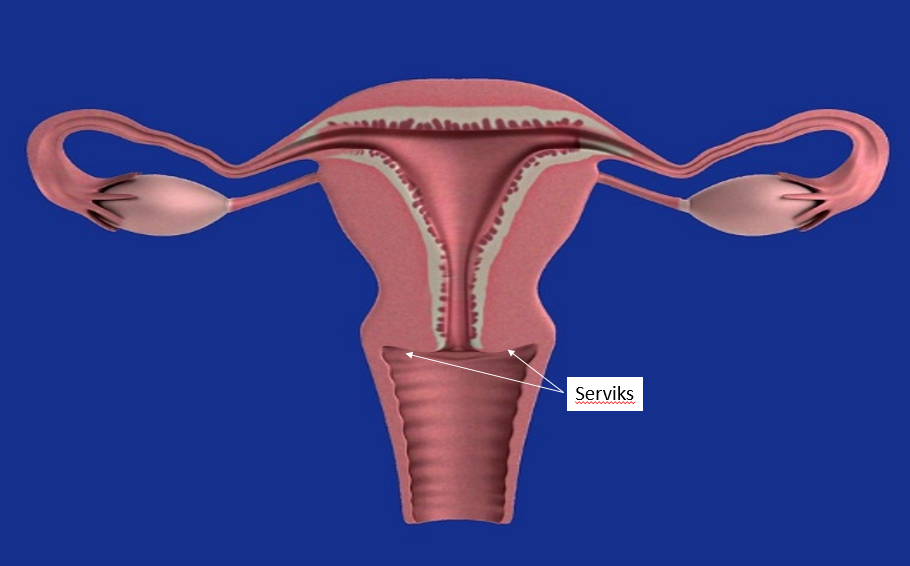
The lowest part of the uterus (uterus), the part where it joins the vagina, is called the cervix (cervix). Cervical cancer develops due to the cancerization of normal cells in this area.
It has been found that cervical cancer is caused by a virus called Human Papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a skin-to-skin contact-transmitted virus with about 200 different types. It is usually transmitted to women through sexual contact.
When the HPV virus is infected, the immune system mostly clears this virus from the body. In a very small group of patients, the virus continues to live in the body for many years and affects normal cells in the cervix, leading to cancer.
Cervical cancer is one of the rare cancers that social screening programs benefit from. You can reduce the risk of developing this cancer by participating in screening programs (smear test, HPV DNA test) or getting HPV vaccines sold in pharmacies.
Symptoms (Signs)
Cervical cancer usually does not give signs at an early stage. Signs seen as the cancer progresses;
- Bleeding after intercourse, bleeding independent of menstrual period and bleeding after menopause
- Watery bloody discharge, sometimes it can be smelly
- Pelvic pain and pain during intercourse
When Should I Go to the Doctor?
If the above-mentioned symptoms have become persistent and concern you, I recommend making an appointment with your doctor. But let's not forget, it is the most rational way to have your regular gynecological examinations.
Reasons
Mutations that develop in the DNA of cells located in the cervix lead to the transformation of healthy cells into abnormal cells. Normal cells grow, multiply, and eventually die. Cancerous abnormal cells, on the other hand, grow, multiply uncontrollably and become immortal. This abnormal collection of cells forms a mass and it is called a tumor. Just as cancer cells can invade healthy tissues around them, they can also spread to distant tissues (metastasis).
The HPV virus can be detected in more than 95% of cervical cancer tissue samples. It is obvious that HPV plays a role in the development of cervical cancer. But the fact that many women carrying the HPV virus do not develop cancer shows that other factors (environmental factors and lifestyle) also contribute to the development of this cancer.
Risk Factors
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexual intercourse at an early age
- The presence of other sexually transmitted infections: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis, HIV-AIDS infections
- The immune system is suppressed
- Smoking
- Using birth control pills for more than 5 years: It is believed that high-risk HPV infections become persistent (continuous), causing an increase in risk.
Protection
- Get information about the HPV vaccine from your doctor
- Have your routine screening tests done
- Choose safe sex: Using condoms during intercourse reduces both HPV transmission and other sexually transmitted infections.< / li>
- Do not smoke: If you do not drink, do not start. If you have been drinking, stop immediately.< / li>
Diagnosis
- Pelvic examination: Your doctor first observes the outer part of your genital area (vulva). It places a special device called a speculum inside your vagina and evaluates the inside of the vagina and the cervix (cervix). Then, he inserts two fingers into the vagina to check for a mass in the vagina and cervix. Some structures that are invisible to the eye are easier to feel with the fingertip. Again, during the procedure, your doctor presses on your stomach with the other hand, compressing the uterus from both sides and trying to find out if there is an abnormal condition. During the finger examination, it is tried to determine whether the adjacent tissues of the cervix, called the parametrium, are being held by the tumor.< / li>
- Colposcopic biopsy: Pathological evaluation is essential to confirm the diagnosis of cancer. The suspicious area in the cervix is examined with a special device called colposcopy, which allows it to be observed better by enlarging the tissues, and a biopsy is performed from this suspicious area. < / li>
Staging
If your doctor decides that you have vulvar cancer, he will want to conduct further tests to see if the cancer has spread to other organs. The stage of cancer is the most important factor that determines the treatment.
- Detailed examination of the pelvic area: To determine the spread of cancer, your doctor may perform a detailed examination of the pelvis and groin.< / li>
- Imaging tests: Advanced tests such as tomography, MRI, PET Sa-CT can be used to determine the spread of cancer.< / li>
- Endocervical curettage: Pathological sampling can be taken from the inner canal of the cervix.< / li>
- LEEP procedure: If the cancer diagnosis cannot be clarified by biopsy or advanced pathological evaluation is needed, it may be desirable to obtain a larger tissue by shaving the cervix. LEEP; It is a procedure performed under operating room conditions, used both in diagnosis and treatment.< / li>
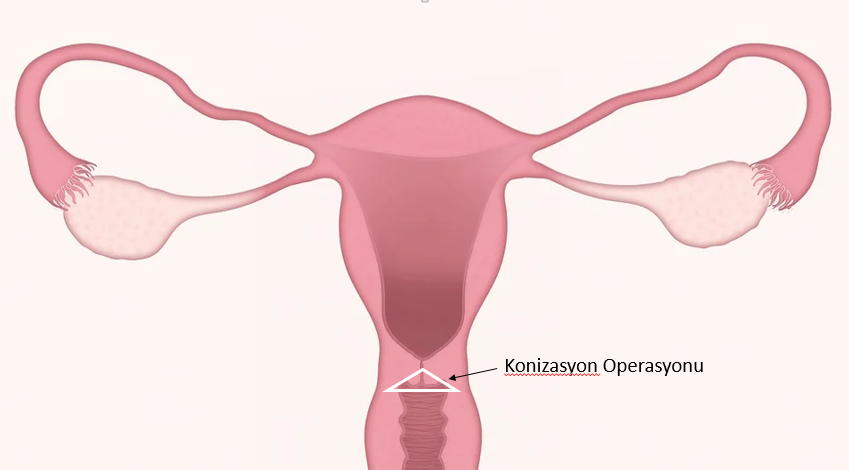
- Conization: Similar to LEEP, it is a procedure performed in the operating room to remove cone-shaped tissue from the cervix. It can be used in both diagnosis and treatment. < / li>
Staging
If your doctor decides that you have cervical cancer, he will want to conduct further tests to investigate whether the cancer has spread to other organs. The stage of cancer is the most important factor that determines the treatment.
- Imaging tests: Advanced tests such as tomography, MRI, PET Sa-CT can be used to determine the spread of cancer.< / li>
- Imaging of the bladder and intestines: If necessary, an image can be taken from the bladder and large intestine with a camera. < / li>
Treatment
The treatment of cervical cancer depends on various factors. The stage of the cancer, other diseases you have, and your preferences will affect the treatment decision. Treatment options are created with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy or a combination of them.
Surgery
The preferred treatment for early stage cervical cancer is surgery. Depending on whether there is a pregnancy desire in the future, the type of surgery is decided.
- Only removal of cancerous tissues: there is a possibility that small cancers will be completely cleared by conization surgery from the cervix. During the conization process, the cervix is removed in the form of a cone. It is one of the methods used in patients who want pregnancy.
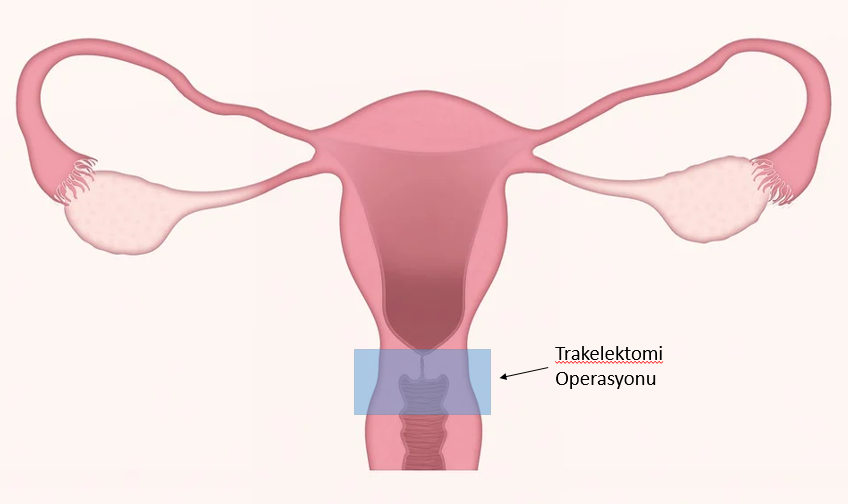
- Removal of the cervix (Trachelectomy): Another method for patients who want to preserve their fertility is a trachelectomy operation. After the cervix and surrounding tissues are removed in this operation, the remaining uterine tissue is sewn back into the vagina and thus the patient is given the chance to achieve pregnancy in the future.< / li>
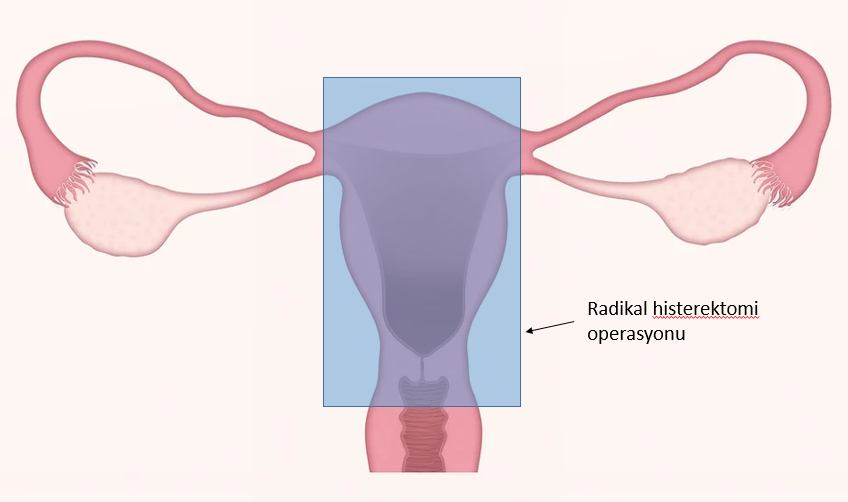
- Removal of the cervix and uterus together (Radical hysterectomy): The method often used in early stage cancers that do not want fertility is a radical hysterectomy operation. The uterus, cervix, parametriums (adjacent tissues of the cervix), lymph nodes and the upper part of the vagina are surgically removed in this operation. < / li>
Radiation Therapy
Radiation is a special type of energy carried by waves and particles. The use of radiation produced in special devices in the treatment of cancer is called radiotherapy or radiation therapy. It is used in cervical cancer in combination with chemotherapy in primary treatment or added after surgery.
It can be used in cervical cancer in the following ways;
- By external route, that is, by external irradiation therapy (External beam radiation therapy)
- By internal route, i.e. by vaginal irradiation (Brachytherapy)
- Or by combining both externally and internally
Summary
In cancer surgery the right surgeon, the right technology and the right pathology are essential. I strongly recommend that you research your surgeon, get opinions from patients he has operated on before, ask about the technologies that will be used in your surgery, and where and how the pathological examination will be performed.



